Understanding WAN Bonding
WAN Bonding is a networking technique that merges several internet connections, such as fibre, cellular, or satellite, into a single logical connection. The result is a faster and more resilient internet experience that can handle high-demand applications even when individual links vary in quality.
True WAN Bonding vs Load balancing and Failover
True WAN bonding operates at the packet level, distributing traffic across multiple links and reassembling it in a data centre using a bonding controller.
Load balancing and failover work at the session level, where each session is tied to a single connection. When that connection degrades or fails, the session is usually interrupted and must be re-established, resulting in dropped calls, frozen video meetings, or disconnected applications.
With true WAN bonding, sessions remain intact even during partial link failures or degradation. In practice, this means no dropped phone calls, no frozen video meetings, and no interruptions to cloud applications, even if one connection slows down or fails.
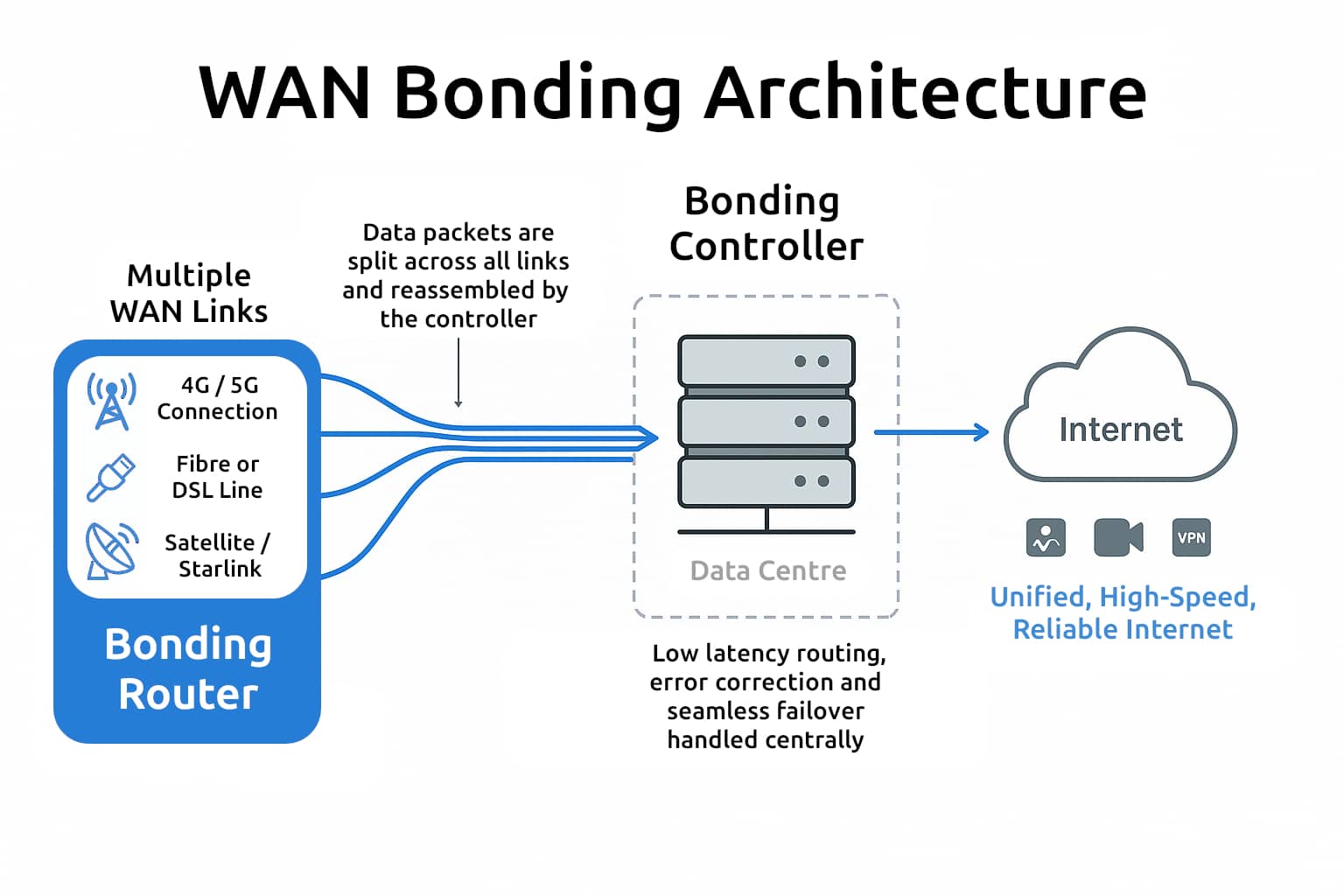
Diagram: Typical WAN Bonding architecture showing multiple links connected to a bonding controller in a data centre.
Because of this architecture, you need more than a single router. A true bonding setup requires an external bonding controller hosted in a high-quality data centre. This controller manages packet sequencing, link health, and latency compensation to deliver smooth, uninterrupted connectivity.
